고정 헤더 영역
상세 컨텐츠
본문
I. 서 론
필자는 환단고기가 말하는 12환국이 동북아시아에 없었다는 글을 썼었다. 백두산과의 지형 위치, 그리고 파내류산과 비서갑 등의 위치를 거론하며, 그 가능성이 없다는 것을 주장하였다. 그런데 한국의 재야 사학가들이 주장하는 12환국의 위치가 동북아시아에 있었다는 어떤 고고학적 근거가 있는가 궁금했다. 그래서 고대로부터의 고고학적 연구를 바탕으로 한번 가늠해 보고자 한다. 물론 이는 필자가 주장하는 북유럽과 유럽에 위치할 가능성이 있는지를 알아 보는 계기도 된다.
II. 한국 재야 사학자들이 추정한 12환국의 위치와 삼한(삼조선)의 위치
아래 지도가 환단고기를 소개하는 재야사학자들의 12환국의 위치 추정이다.

한국의 재야사학자들이 주장하는 12환국의 위치 (자료 : STB 상생방소 유튜브 자료)
어떤 근거로 위와 같이 추정했는지 알 수 없지만, 이와 관련하여 연구와 학문적 논쟁이 있어야 할 것이다. 아니면 국수주의자의 국뽕에 지나지 않는 것이 된다. 필자는 우선 양운국, 일군국이 강족과 저족이라 한 그들이 소개한 자료를 보았는데, 과연 강족과 저족의 위치가 상기 지도 위치와 같은지 의문스럽다. 역사를 왜곡하고 있는 중공사가들도 강족과 저족의 위치를 중공 서부로 보고 있는 것으로 안다. 또한 수밀이국은 수메르문명으로 추정하는데, 상기 위치에 어떤 고고학적 자료가 있는지 의문스럽다. 환단고기에 의하면 12환국은 남북 오만리 동서 2만리에 걸쳐 있다고 하는데, 이와 같은 거리상으로도 상기 지도는 맞지 않는다. 따라서 상기 위치를 주장하는 분들은 좀 더 과학적으로 근거를 제시할 필요가 있다.

한국의 재야사학자들이 주장하는 3조선의 위치 (자료: STB 상생방송, 유튜브 자료)
환단고기에서 말하는 삼한 (진한, 마한, 번한)의 위치를 환단고기를 진서로 주장하는 재야사학자분들은 상기 지도처럼 추정하는 것으로 보인다. 그런데 이에 대한 근거가 있는지 궁금하다.
중공사가들이 주장하는 중국의 위치도 하나라의 유물이 나타나지 않는 점을 들어 의문시된다는 주장이 있다. 하나라는 흉노의 조상이라 하는데, 중공 사가들이 주장하는 흉노제국은 북쪽에 있다. 그럼 상기 지도의 하나라의 위치가 당요와 우순임금의 위치가 되는 것으로 추정되는데, 저윽이 의문스럽다.
또한 상기 지도의 마한, 진한, 번한의 3한의 위치도 어떤 근거가 있는지 궁금하다. 중국사 기록에 의한 후대의 마한 진한 변한에 관한 기록은 비록 시대가 차이가 있지만, 상기 위치 추정과 매우 다르다. 이를 설명할 수 있어야 한다. 과거 오래된 역사이므로, 유물의 과학적 분석에 의한 뒷받침이 있어야 할 것이다.
12환국은 기원전 7197년 시작하여 기원전 5000년경 12환국이 성립되었다 한다. 이는 대체로 신석기시대에 속한다. 그러나 이들 문명이 있기 전에 어느 정도 준비기간이 있었으리라 판단된다. 그래서 구석기시대부터 인류의 이동 역사를 알면 보다 그 정확한 위치를 가늠할 수 있을 것으로 판단된다. 따라서 구석기 시대부터 인류의 이동역사를 알아 보고자 한다. 물론 오래된 역사이기 때문에 유물과 인간의 유전자 분석이 주를 이루게 된다.
III. 초기 구석기시대 (50K- 20K BP) 인류의 이동 역사
초기 구석기시대는 지금부터 5만년전에서 2만년전까지의 역사를 말한다. 이 시기는 마지막 빙하기이전의 시기이므로 단지 참고 삼아 알아 보고자 한다. 인류의 기원에 대한 연구는 필자의 관심사항이 아니다. 단지 구석기 시대의 어느 정도의 인류이동 역사를 알면 이후의 중기 말기 구석기 시대의 상황을 더 이해할 수 있기에 알아 보고자 한다.
아래 지도는 아프리카에서 출발한 인류의 이동경로를 말하고 있다. 지금부터 5만년전부터 2만년전까지의 이동 경로를 나타내고 있다. 아래 지도는 육로로 이동한 경로에서 시베리아에 와서 서쪽으로 이동하여 유럽으로 가는 경로와 동북 시베리아로 가다가 다시 몽고지역으로 내려와 Mal'ta지역으로 내려오는 경로와 남부 아시아를 거쳐 동남아시아를 거쳐 산동지방(Tianyuan)에 이르는 경로를 보여 준다. 이중에서 우리가 동북아시아에 관심을 가지고 본다면, 동북시베리아에서 내려오는 경로와 동남아시아에서 중국 남부를 거쳐 산동지방에 이르는 경로를 주의하여 살펴보아야 할 것이다.

Differentiation_after_dispersal_out_of_Africa_in_the_Early_Upper_Paleolithic_(45,000–20,000_years) (source : Wikipedia)
동아시아에서 제일 오래된 인류의 흔적은 산동지방에서 발견된 Tianyuan man으로서 4만년전의 인류로 판명되었다. 특히 위지도의 AR33K는 아무르강지역에서 발견된 여성으로 33000년전의 인류로 판명된 것을 말하며, 34,000년전의 Salkhit지역(북동몽고지역)의 인류와 함께 Tianyuan man과 75% 유전자를 공유하였으며, 나머지 25%는 북시베리아인류의 유전자를 보이고 있다 한다. 즉 이들지역이 마지막 빙하기전까지 하나의 인척그룹이 아닌가 하는 연구를 말하고 있다. (아래 자료 참조)
"In 2003, another research group found the remains of Tianyuan man, and to this day the individual's DNA is the earliest known ancient human genome from East Asia. Thanks to Tianyuan man and other archaeological findings, researchers know that modern humans lived in northern East Asia as early as 40,000 years ago. This region includes the Mongolian Plateau, northern China, Japan, the Korean Peninsula and the mountainous regions of the Russian Far East.
(번역) 2003년 또 다른 연구그룹은 Tianyuan man의 유물을 발견했는데, 오늘날까지 이 개인의 DNA는 알려진 가장 오래된 동아시아 인간 게놈이다. Tianyuan man과 다른 고고학적 발견으로, 연구자들은 현대 인류가 동북아시아에 최대 4만년전에 살았다는 것을 알게 되었다. 이 지역은 몽골고원, 중공북쪽, 일본, 그리고 한반도와 극동 러시아의 산간지역까지 포함된다.
Recent studies have shed light on the population dynamics of East Asia from about 9,000 years ago to recent historical times, but less is known about what happened from 40,000 to 9,000 years ago, Fu said.
(번역) 최근의 연구에 의하면, 약 9천년전부터 최근 역사적 기간까지 동아시아에 인구 역동성이 있었다는 것을 밝혀주고 있다. 그러나 4만년부터 9천년전까지 무슨 일이 있었는지 알려진 것이 적다고 Fu(=중국의 고고학 유전자학자, 이 article의 주요 정보 제공자)는 말했다.
.............................
The ancient DNA analysis revealed that the oldest person they studied, a Pleistocene female known as AR33K, who lived about 33,000 years ago in the Amur region (AR stands for Amur and 33K stands for 33,000), had the highest genetic similarity with Tianyuan man, compared with all other published ancient and modern individuals from East Asia, Fu said.
(번역) 고대 DNA분석에 의하면, 연구된 가장 오래된 인간은 AR33K로 알려진 홍적세의 여성인데, 그녀는 약 33000년전에 아무르지역에 살았다. (AR은 Amur를 의미하며, 33K는 33,000 년을 의미한다.) 그리고 그녀는, 다른 모든 공개된 고대 및 현대 동아시아인들과 비교하여, Tianyuan man과 가장 근접한 유전적 유사성을 가졌다고 Fu는 말했다.
Another ancient woman, whose DNA was described in a previous study, lived about 34,000 years ago in Salkhit Valley in northeastern Mongolia. This woman was found about 720 miles (1,159 kilometers) from AR33K and about 692 miles (1,114 km) from Tianyuan Cave. A 2020 study in the journal Science found that the Salkhit woman shared 75% of her genetics with Tianyuan man and 25% with another ancient East Asian group that lived along the Yana river in North Siberia. Given that both AR33K and the Tianyuan man share about 75% of their DNA with the Salkhit woman, it's possible that these people were part of related groups that traveled across East Asia for at least 7,000 years, Fu told Science magazine.
(번역) 이전의 연구에서 그 DNA가 언급된 다른 고대여인은 북동몽고지역의 Salkhit 계곡에 약 34000년전 살았던 여인이다. 이 여인은 AR33K로부터 720마일(1159km) 그리고 Tianyuan 동굴로부터 692마일(1114km) 떨어진 곳에서 발견되었다. 2020년 Science 저널의 연구에 의하면, Salkhit여인은 Tianyuan man과 75%의 유전자를 공유하고 있었으며, 북 시베리아의 Yana 강가에 살았던 다른 고대 동아시아그룹과 25%를 공유하고 있다. AR33K와 Tianyuan man이 Salkhit여인과 75%의 유전자를 공유한 것을 고려하면, 이 사람들이 적어도 7천년동안 동아시아를 여행하는 인척관계의 그룹의 일부일 수 있다고 본다고 Fu는 Science 매거진에 말했다.
"However, unlike the Salkhit woman, AR33K does not have more Yana-related ancestry than Tianyuan man does, the researchers wrote in the new study. "This probably indicates that Tianyuan/AR33K ancestry was widespread before the LGM in northern East Asia, both geographically, from northern China to Mongolia and the Amur region, and temporally, from 40,000 to 33,000 years ago," Fu told Live Science in the email."
(번역) 그러나, Salkhit여인과 달리, AR33K여인은 Tianyuan man이 그랬던 것보다 Yana관련 조상인자를 더 가지고 있지 않았다. 그래서 새로운 연구에서 연구자들은, 이것이 Tianyuan/AR33K 조상들이 동북아시아에서 마지막 절정 빙하기(LGM)이전에 널리 퍼져 있던 것이 아닌가 한다. 지역적으로 북중공에서 몽고까지 그리고 아무르지역까지 시기적으로는 4만년전에서 33000년전까지 펴져 있던 것으로 보인다고 Fu는 Live Science에 이메일로 말했다.
(source ; AR33K, Live Science, 인용출처 : 필자의 티스토리 블로그 (lostcorea), 카테고리, 고대 동아시아)
그러나 빙하기가 끝나는 19000년전에 아무르지역에 새로운 인류집단이 나타났다고 하였다. (아래 자료 참조) 그리고 지금의 아무르지역 인류는 14000년전 (또는 8000년전) 인류가 계속 이어온 것으로 연구된다 한다. (아래 자료 참조)
"Oldest "new person"
Another standout individual from the study, AR19K, who lived in the Amur region about 19,000 years ago toward the end of the LGM, caught the researchers' attention. AR19K's genetic ancestry is distinct from Tianyuan and AR33K, "indicating a potential population shift," Fu said. In other words, while AR33K and Tianyuan passed on some genes to modern East Asians (Fu called them "basal to all East Asians"), the populations they came from vanished at some point during the LGM.
(번역) 연구에서 또 하나의 눈에 띄는 개인인, 마지막 절정 빙하기(LGM) 말기 19000년전에 아무르지역에 살았던 AR19K가 연구자들의 주의를 끌었다. AR19K는 유전자 조상은 Tianyuan과 AR33K와 구별되는데, 이는 잠재적 인구이동을 의미한다고 Fu는 말했다. 다른 말로 말하면, AR33K와 Tianyan은 현대의 동아시아인 (Fu는 이들을 모든 동아시아인의 토대가 되는 것으로 말함) 몇몇 유전인자를 전한 반면, AR19K 이들은, 마지막 절정 빙하기(LGM)의 어느 시점에서 사라졌다가 왔다.
In fact, AR19K is "the earliest northern East Asian yet identified," meaning this individual is ancestral to ancient northern East Asians. The identification of this northern East Asian ancestor "indicates that north-south genetic separation in East Asia is as early as 19,000 years ago, 10,000 years earlier than previously discovered," Fu said.
(번역) 사실, AR19K는 이제까지 확인된 동북아시아인 중 가장 오래된 사람인데, 이는 이 개인이 고대 동북 아시아인의 조상이라는 것을 의미한다. 이러한 북쪽의 동아시아인 조상의 확인은 19000년전 (기존의 발견보다 10000년이 더 빠른)에 동아시아에서 북과 남이 유전적으로 분리되는 것을 나타낸다고 Fu는 말했다.
Some East Asia areas have had remarkable genetic ties to the past, the younger samples revealed. For instance, researchers previously thought that modern populations in the Amur region had an 8,000-year genetic continuity with Neolithic foragers and farmers who lived at Devil's Gate cave in Far Eastern Russia and the Amur region. But the new analyses showed that this continuity goes back 14,000 years, or "6,000 years earlier than previously proposed," Fu said."
(번역) 몇몇 동아시아지역은, 보다 후대의 샘플이 보여주는 것처럼, 과거와 괄목할만한 유전적 연결관계를 가졌다. 예를 들면, 연구자들은 과거 아무르지역의 현대인들은 신석기시대의 약탈자들과 극동러시아와 아무르지역에 있는 Devil's Gate 동굴에 살았던 농업인들과 8천년의 유전적 연속성이 있다고 생각했다. 그러나 새로운 분석들은 이 연속성이 14000년전으로, (기존의 제시보다 6천년이 더 거슬러 올라가는) 올라간다고 Fu는 말했다.
(source ; AR33K, Live Science, 인용출처 : 필자의 티스토리 블로그 (lostcorea), 카테고리, 고대 동아시아)
그러나 북몽골지역의 Kharaa gol (카라골, 우리말?) 강에 있는 Salkhit지역의 인류는 일부가 아프리카와 관련이 없는 인류라고 나타난다고 한다. (아래 자료 참조)
"Salkhit (Mongolian: Салхит, "windy") is a settlement in the Khongor sum (district) of Darkhan-Uul Province in northern Mongolia.
Salkhit is located on the Kharaa gol river (a right tributary of the Orkhon river), 13 km south of the center of the sum of Khongor, and 33 km south of the aimag capital Darkhan.
............
Prehistory[edit]
An archaic Homo sapiens skullcap with archaic features similar to those of Neanderthals, Homo erectus and Asian archaic Homo sapiens was found near Salkhit in 2006 during gold mining operations at depth 5–6 m.[1] Original estimates dated the skullcap to about 22,100 years old, but later re-dating in 2010 indicated 23,630 BP.[1][2] In 2019, the Salkhit skull was again radiocarbon dated, analyzing hydroxyproline in bone-extracted collagen, placing it in the range 34,950–33,900 cal BP.[3] Despite its archaic features, genetic reconstruction of ancient DNA from the skull indicates the specimen falls on a novel branch of mtDNA haplogroup N, one of two basal haplogroups ancestral to all non-African populations. Application of a molecular clock to the mtDNA sequence yielded a date for the skull of 12,910 to 39,410 years BP.[3]
(번역) 네안데르탈인 Homo erectus와 유사한 고대의 Homo sapens와 아시아 고대 Homo sapiens의 머리덮개뼈가 2006년 Salkhit에서 깊이 5-6m의 금광작업 중에 발견되었다. 이 유골들은 처음에는 22,100년이 된 것으로 추정되었으나, 이후 2010년 재측정한 것은 23,630년전의 것으로 밝혀졌다. 2019년에는 Salkhit 유골은 유골에서 추출된 콜라겐의 hydroxyproline을 분석한 방사성 탄소 측정 결과 34,950-33,9000년전으로 재추정되었다. 이러한 고대의 양상에도 불구하고, 유골로부터의 고대 DNA의 유전적 재구성을 해보면, 모든 비아프리카 인구들에게 필수적인 haplogroups 조상 인자 둘중의 하나인, haplogroup N의 mDNA 귀족계열에 속하는 종으로 나타난다. mDNA배열의 분자 구조 분석을 해보면, 유골의 연대는 12,910년전에서 39,410년전으로 추정된다.
(soure : Salkhit, wikipedia, 인용출처: 필자의 티스토리 블로그 (lostcorea), 카테고리, 고대 동아시아)
IV. 중기 구석기 시대 (24 K - 16K BP) : 고대북유라시언(Acient North Eurasians, ANE)
위에서 살펴본 지도에서 Mal'ta지역에서 발견된 Mal'ta boy 유해는 고대 북유라시언으로 분류되며, 이들이 서쪽으로 이동하여 중앙아시아와 유럽으로 이동한 인류가 되며, 일부는 동쪽으로 이동하여 북아메리카까지 이동하는 인류로 연구되어진다. 이들은 고대 사카인류로 분류되기도 하므로, 여기서 보다 자세히 살펴 보고자 한다. 그리고 이들과 동아시아인 특히 바이칼호수와 아무르지역과 관련한 관계가 어떤지 알아 보고자 한다. 이는 후일 기원전 5000년경 12환국이 이 지역에 있었는지 알아 보는 과정의 하나라 판단한다.

고대북유라시언(Ancient Norh Eurasians, ANE)(24000-16000년전)의 위치 (자료: Wikipedia)
Ancient North Eurasians은 Mal'ta-Buret culture (24000 BP (Before Present))와 시베리아의 Afontova Gora지역의 초기 구석기인들과 깊이 연관되어 있다.
유전적 연구에 의하면, 고대북유라시언(ANE)은 동북쪽 시베리아끝 북극해에 닿아 있는 사하공화국이 있는 Yana culture(32000 BP)로 대표되는 고대 북 시베리아인(Ancient North Siberians, ANS)과 밀접하게 연관되어 있다. (아래 자료 참조) 즉 ANE는 ANS의 후손으로 간주되거나, 혹은 ANE와 ANS가 서로 밀접하게 연관되어 있지만 다른 sister lineages일 수 있는 것이다. 그런데 이들 모두 즉 ANE와 ANS는 초기 서부 유라시언 수렵인 계열 (Kostenki-14(돈강유역, 4만년전)로 대표됨)과 초기 동부유라시언 (Tianyuan man(산동지방, 4만년전)으로 대표됨)으로부터 비롯되었다 한다. (아래 자료 참조) 또한 초기 동부 유라시언이 초기 서부유라시언으로 이동한 것으로 보인다. ANE와 ANS는 16-35%의 초기 동부유라시언 인자와 65-84%의 초기 서부유라시언의 인자를 가졌다. (아래 자료 참조)
"In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) is the name given to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the people of the Mal'ta–Buret' culture (c. 24,000 BP) and populations closely related to them, such as the Upper Paleolithic individuals from Afontova Gora in Siberia.[6][7] Genetic studies indicate that the ANE are closely related to the Ancient North Siberians (ANS) represented by two ancient specimens from the preceding Yana Culture (c. 32,000 BP). The ANE can either be considered to descend from the earlier ANS population, or that both ANE and ANS are closely related, albeit differentiated, sister lineages, with both having originated from an 'Early West Eurasian' hunter-gatherer lineage (represented by Kostenki-14, c. 40,000 BP),[8] which absorbed an 'Early East Eurasian' population (represented by the Tianyuan man, c. 40,000 BP). The ANS and ANE each derive between 16% to 35% of their ancestry from an Early East Eurasian lineage and between 65% to 84% from an Early West Eurasian lineage.[a][b][9][10][11][12][13][14]
(번역) 고고학적 유전자학으로 말하면, 고대 북유라시언(Ancient North Eurasian, ANE)은 Mal'ta-Buret' culture (24000년전) 사람들과 시베리아의 Afontova Gora의 초기 구석기시대의 사람들과 밀접하게 관련된 사람들의 계통을 나타내는 조상들의 요소를 말한다. 유전학적 연구에 의하면, ANE는, 앞서 있는 Yana culture(32000년전)의 두 고대 표본에 의해 대표되는 고대 북시베리아인 (Ancient North Siberians, ANS)과 밀접하게 관련되어 있음을 보여 준다. ANE는 보다 이전 시기의 ANS 사람들의 후손으로 간주 되거나, 또는 ANE와 ANS가, 비록 다를지라도, 서로 밀접하게 연관되어 있어 sister lineages로 간주된다. 그런데 이들 ANE, ANS는 초기 서유라시언 수렵인그룹 계열 (4만년전 Kostenki-14 (돈강유역)로 대표되는)로부터 연유된 것으로 것이다. 그런데 초기 서유라시언 수렵인 그룹은 초기 동유라시언 인구 (4만년전, Tianyuan man으로 대표되는)를 흡수한 것으로 보인다. ANS와 ANE는 각각 16-35%의 초기 동유라시언 계열의 조상유전자와 65-84%의 초기 서유라시언 계열의 조상유전자를 가지고 있다.
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park
의미있는 ANE 조상인자가 북유럽, 남아시아, 중앙아시아, 시베리아 뿐만 아니라, Native Americans에서도 발견된다. (아래 자료 참조)
"Significant ANE ancestry can be found in Native Americans, as well as in regions of northern Europe, South Asia, Central Asia, and Siberia. It has been suggested that their mythology may have featured narratives shared by both Indo-European and some Native American cultures, such as the existence of a metaphysical world tree and a fable in which a dog guards the path to the afterlife.[17]
(번역) 의미있는 ANE 조상 유전자가 북유럽, 남아시아, 중앙아시아, 그리고 시베리아 뿐만 아니라, Native Americans에서도 발견된다. 이들의 신화에서도 인도유럽인과 Native Americans사이에 공유되고 있다. 예를 들어, 형이상학적 world tree의 존재나 내세로 가는 길에 개가 지키는 우화 같은 존재들이다.

The "Ancient North Eurasian" (ANE) network, consisted of several Paleolithic Siberian samples and contributed ancestry towards a wide variety of populations across Eurasia. (source : Wikipedia)
ANE계열은 중앙 시베리아에서 마지막 빙하 절정기인 24000년전에 살았던 Mal'ta Boy와 연관되어 있다. Yana 지역 샘플과 Afontova Gora인들과 함께 Anicent North Siberians (ANS)라 언급된다. (아래 자료 참조)
"The ANE lineage is defined by association with the "Mal'ta boy" (MA-1), the remains of an individual who lived during the Last Glacial Maximum, 24,000 years ago in central Siberia, discovered in the 1920s. Together with the Yana Rhinoceros Horn Site samples, and Afontova Gora individuals, they are collectively referred to as 'Ancient North Siberians'.[18][19]
(번역) ANE 계열은 Mal'ta boy(MA-1)와 관련되어 정의되는데, 중앙 시베리아에서 24000년전, 마지막 절정 빙하기동안에 살았던 개인의 유해가 1920년대 발견되었다. Yana Rhinoceros Horn site샘플 그리고 Afontova Gora 개인들과 함께, 그들은 집단적으로 고대 북시베리아인(Ancient North Siberians)이라 일컬어진다.
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park
현대인구에서 발견되는 ANE 조상인자는 주로 Afontova Gora지역 인구와 관련되어 있다. (아래 글 참조)
"The Ancient North Eurasians represent a distinct cluster of genetic diversity within the larger Eurasian gene pool, which is deeply related to Paleolithic and Mesolithic European hunter-gatherers.[22] It is suggested that the ANE ancestry found among modern human populations was largely contributed from a population linked to Afontova Gora (AG-3), rather than Malta (MA-1) or Yana.[23] "
(번역) 고대북유라시언 (ANE)은 보다 광범위한 유라시언 유전자풀에서 유전적 다양성을 지닌 구별된 클러스터를 대표한다. 유라시언 유전자풀은 구석기와 중석기 유럽 수렵인그룹과 깊이 관련되어 있다. 현대인구에서 발견된 ANE조상인자는, Malta(MA-1)나 Yana보다는 Afontova Gora(AG-3)에 연계된 인구에 보다 광범위하게 연유한다.
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park
Malta와 Yana지역 유전인자 모두 유럽 수렵인계열 (돈강의 Kostenki-14)과 Basal East Asian인 산동지방의 Tianyuan man 계열의 혼합으로 나타난다. 그러나 ANE로부터 Tianyuan 이나 현대 동아시아인으로의 유전적 흐름은 아무 증거가 발견되지 않았다. (아래 글 참조). 또 다른 연구에 의하면, 산동지방의 Tianyuan man과 동부유럽수렵인 (Eastern Europan Hunter Gatherers (EHG) 사이에 높은 유사성이 확인되었다. EHG그룹은 ANE조상의 인자를 상당한 정도 받았으며, Tianyuan-like 조상의 인자는 12.9%로 추정된다. (아래 글 참조)
"Yang et al. 2020a,b, corroborated that both the Malta and Yana specimens formed from the merger of a sister lineage of the 'European hunter-gatherer' Kostenki-14, and from a lineage contemporary to the 'Basal-East Asian' Tianyuan man, while finding no evidence for a reversed geneflow from ANE into Tianyuan or modern East Asians.[34][35] Other studies could reproduce a shared affinity between ANE and the Tianyuan man (or other Upper Paleolithic East/Southeast Asian specimens), and also confirmed higher affinity between the Tianyuan man and Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers (EHG), which received significant amounts of ANE ancestry.[27] The 'Basal East Asian' (Tianyuan-like) ancestry among EHGs (Sidelkino) has been estimated to be around 12,9%.[36] "
(번역) Yang과 그외 공동연구자들은 Malta와 Yana표본은 유럽인 수렵인 (European Hunter-Gatherer, 돈강유역의 Kostenki-14)의 자매 계열과 Basal-East Asian인 Tianyuan man(산동지방)의 당대 계열과의 혼합으로 이루어졌다. 반면, ANE로부터 Tianyuan 또는 동아시아인으로의 역방향의 유전자흐름은 그 증거를 발견하지 못했다. 다른 연구들은 ANE와 Tianyuan man (또는 다른 초기 구석기시대 동아시아인/동남아시아인 표본) 사이의 유사성을 도출하고 있으며, 또한 Tianyuan man과 Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers(EHG)사이에 높은 친연성을 확인했다. 그런데 EHG는 상당한 정도의 ANE 조상인자를 가졌다. EHGs(Sidelkino)중에서 Tianyuan같은 Basal East Asian 조상인자는 약 12.9%로 추정되었다.
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park
유전자 연구에 의하면, ANE 구성요소는, 구석기 시대 한참 후에, Yamnaya culture에 관련된 사람들에 의해 서유럽으로 이동된 것으로 말한다. 현대의 유럽인의 10-20%가 되는 것으로 보고된다. 초기의 ANE 조상인자는, 구석기시대에 동유럽 수렵인그룹(Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers(=EHG)과 상호관계로 인하여, 유럽의 수렵인 그룹인들에서 발견된다. 동유럽 수렵인그룹은 스칸디나비언 수렵인 (Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers(=SHG) 그룹을 초래했다. (아래 글 참조)
"Genomic studies also indicate that the ANE component was brought to Western Europe by people related to the Yamnaya culture, long after the Paleolithic.[43][6] It is reported in modern-day Europeans (10%–20%).[43][6] Earlier ANE ancestry is found in European hunter-gatherer populations through Paleolithic interactions with Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers, which resulted in populations such as Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers. [47] Western Hunter-Gatherers of the Villabruna cluster also carried the Y-haplogroup R1b, derived from the Ancient North Eurasian haplogroup R*, indicating "an early link between Europe and the western edge of the Steppe Belt of Eurasia."[48] "
(번역) 유전자 연구에 의하면, ANE 구성요소는, 구석기 시대 한참 후에, Yamnaya culture에 관련된 사람들에 의해 서유럽으로 이동된 것으로 말한다. 현대의 유럽인의 10-20%가 되는 것으로 보고된다. 초기의 ANE 조상인자는, 구석기시대에 동유럽 수렵인그룹(Eastern European Hunter-Gatherers(=EHG)과 상호관계로 인하여, 유럽의 수렵인 그룹인들에서 발견된다. 동유럽 수렵인그룹은 스칸디나비언 수렵인 (Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers(=SHG) 그룹을 초래했다. Villabruna cluster같은 서유럽 수렵인그룹(Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG)) 역시 ANE의 haplogroup R*로부터 유래된 Y-haplogroup R1b유전자를 가지고 있다. 이는 유럽과 유라시아 서쪽끝 초원벨트사이에 일찍부터 연관관계가 있음을 의미한다.
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park
고대의 Tianyuan man과 현대의 동부/동남아시아인들은 초기 구석기시대 서유라시언이나 ANE관련 인자가 없는 것으로 나타난다. 이는 이들이 초기 구석기시대 인구유입에 저항했다는 것을 의미한다. (아래 글 참조)
"The Ancient Tianyuan Man and modern East/Southeast Asian populations were found to lack Upper Paleolithic Western Eurasian or ANE-related admixture, suggesting "resistance of those groups to the incoming UP population movements", or alternatively a subsequent reexpansion from a genetically East Asian-like population reservoir.[50] "
(번역) 고대의 Tianyuan man과 현대의 동부/동남아시아인들은 초기 구석기시대 서유라시언이나 ANE관련 인자가 없는 것으로 나타난다. 이는 이들이 초기 구석기시대 인구유입에 저항했다는 것을 의미한다. 또는 유전적으로 동아시아인 계통의 남은 인구가 뒤이어 재팽창한 것을 의미할 수도 있다.
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park
V. 고대북유라시언 (Ancient North Eurasians (ANE))의 서쪽 이동 (15000 BP - 9000 BP)
고대 북유라시아인 (ANE)이 일부는 동쪽으로 가서 북아메리카로 갔지만, 또한 서쪽으로 가서 유럽에 진출했다 한다. (아래 지도 참조) 그러나 여기서는 동아시에 12환국이 있었는가를 검토하는 주제이므로, 서쪽으로 가서 유럽에 진출한 것은 구체적인 자료 검토를 생략하고, 간단히 넘어 가고자 한다. 12환국이 유럽에 있었는가는 또 하나의 큰 주제이므로 별도의 글로 도전해 볼 생각이다. 19000년전 빙하기가 끝나고 중석기인 대략 15000년전부터 고대북유라시아인들은 서쪽으로 진출한다.

Schematic_ethnogenesis_of_the_Eastern_Hunter-Gatherers_(EHG) (source : Wikipedia)
1. Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) (15,000 BP - )
지금부터 15000년전에 고대북유라시아인(ANE)들은 서쪽으로 가서 동부수렵인그룹(Eastern Hunter-Gatherer=EHG)을 이룬다. 이들은 서부 러시아, 흑해위지역, 핀란드지역 등을 포함한다.
고고학적으로, 동부수렵인그룹(Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG) 단어는 때로는 동부유럽수렵인그룹 (East European Hunter-Gatherer 또는 Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer)으로 불리는데, 동부유럽의 중석기 수렵인 그룹을 나타내는 명백한 조상구성요소이다. (아래 글 참조)
"In archaeogenetics, the term Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), sometimes East European Hunter-Gatherer, or Eastern European Hunter-Gatherer is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents Mesolithic hunter-gatherers of Eastern Europe.[3] "
(source : Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lainfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유럽)
동부수렵인그룹 (EHG)의 유전적 모습은 시베리아로부터 온 고대북유라시아인 (ANE)로부터 주로 도출되고, 두번째로 보다 약한 유럽의 서부수렵인그룹(Western Hunter-Gatherer(=WHG) 요소가 있다. 그럼에도 불구하고, ANE와 EHG의 조상 구성요소 관계는 아직 잘 이해되지 못하는데, 시간적 공간적 차이를 연결해주는 샘플들이 부족하기 때문이다. (아래 글 참조)
"The Eastern Hunter Gatherer genetic profile is mainly derived from Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) ancestry, which was introduced from Siberia,[4] with a secondary and smaller admixture of European Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG).[5][6] Still, the relationship between the ANE and EHG ancestral components is not yet well understood due to lack of samples that could bridge the spatiotemporal gap.[5] "
(source : Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lainfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유럽)
중석기시대에 동부수렵인그룹(EHG)은 발틱해에서 우랄산맥, 그리고 흑해 카스피해 위 초원지역(Pontic-Caspian steppe) 에 걸쳐 살았다. 스칸디나비아 수렵인그룹 (Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (=SHG))과 서부수렵인그룹(Western Hunter-Gatherer (=WHG))과 함께, 동부수렵인그룹(EHG)은, 초기 Holocene(마지막 빙하기 이후 현재에 이르는 기후시기, BC 9700년 시작) 유럽, 빙하기이후 시기에, 주요한 3개의 유전자그룹중 하나를 형성한다. WHGs와 EHGs 사이의 경계는 대강 다뉴브강 하류로부터 드네프르강의 서쪽 숲을 따라 북쪽으로 발트해 서쪽지역에 이른다. (아래 글 참조)
"During the Mesolithic, the EHGs inhabited an area stretching from the Baltic Sea to the Urals and downwards to the Pontic–Caspian steppe.[7] Along with Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherers (SHG) and Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG), the EHGs constituted one of the three main genetic groups in the postglacial period of early Holocene Europe.[8] The border between WHGs and EHGs ran roughly from the lower Danube, northward along the western forests of the Dnieper towards the western Baltic Sea.[9] "
(source : Eastern Hunter-Gatherer (EHG), Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lainfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유럽)
아래 유전자 분석기간은 14000 - 9000 BP (Before Present)인데, EHG 분포를 나타내고 있다.

Genetic_ancestry_of_hunter-gatherers_dated_between_14_ka_and_9_ka_(EHG) (source : Wikipedia)
2. Western Hunter Gatherers(WHG) (15000 BP - 5000 BP)
중서부유럽을 포함한 서부수렵인그룹(Western Hunter-Gatherers(WHG))은 지금부터 15000년전에서 5000년전까지, 즉 BC 13000- BC 3000까지 존재한 중석기시대 그룹이다.
고고학적으로, 서부수렵인그룹 (Western Hunter-Gatherer(WHG)은 West European Hunter-Gatherer, Western European Hunter-Gatherer, Villabruna cluster 또는 Oberkassel cluster로 불리는데, 15000-5000 BP 기간중에 활동했다. 이들은 현대 유럽인들의 분명한 조상들로서, 중석기 수렵인그룹인들의 후손을 나타내는데, 서부유럽, 남부 유럽, 중부유럽, 서쪽의 영국 섬들로부터 동쪽으로 카르파티언산맥까지, 마지막 빙하기 절정 시기가 물러간 뒤에 따른 것이다. (아래 글 참조)
"In archaeogenetics, the term Western Hunter-Gatherer (WHG), West European Hunter-Gatherer, Western European Hunter-Gatherer, Villabruna cluster, or Oberkassel cluster (c. 15,000~5,000 BP) is the name given to a distinct ancestral component of modern Europeans, representing descent from a population of Mesolithic hunter-gatherers who scattered over Western, Southern and Central Europe, from the British Isles in the west to the Carpathians in the east, following the retreat of the ice sheet of the Last Glacial Maximum.[2] "
(Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG), Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lainfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유럽)
아래지도는 14000-9000 BP 기간의 서부수렵인그룹(WHG)의 분포를 보여 주고 있다.

Genetic_ancestry_of_hunter-gatherers_dated_between_14_ka_and_9_ka_(WHG_highlighted) (source : Wikipedia)
3. Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG) (14000 - 9000 BP)
SHGs는 WHGs와 EHGs와 거의 같은 비율의 혼합이다. 전유럽에 걸쳐 한때 주요 인구였던 WHGs는, 초기 신석기시대의 초기유럽농부그룹 (Early European Farmers (=EEFs)의 계속된 팽창에 의해, 대부분 교체된다. EEFs는 중기 신석기시대에 다시 대두한다. 말기 신석기시대와 초기 청동기시대에는 Pontic-Caspian Steppe지역으로부터 Western Steppe Herdes (WHGs)가 대대적으로 팽창하여 WHGs을 더 이동시킨다. 현대인구중에는 WHG 조상 유전자는 동부발틱의 인구들에게 매우 흔하다. (아래 글 참조)
"SHGs were in turn a nearly equal mix of WHGs and EHGs. Once the main population throughout Europe, the WHGs were largely displaced by successive expansions of Early European Farmers (EEFs) during the early Neolithic, but experienced a resurgence during the Middle Neolithic. During the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, Western Steppe Herders (WSHs) from the Pontic–Caspian steppe embarked on a massive expansion, which further displaced the WHGs. Among modern-day populations, WHG ancestry is most common among populations of the eastern Baltic.[4] "
(Western Hunter-Gatherers (WHG), Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lainfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유럽)
신석기시대 (9600-4000 BC)의 Early European Farmers(EEF)의 유럽진출 상황은 아래 지도와 같이 나타난다.

Expansion_of_farming_in_western_Eurasia,_9600–4000_BCE (source : Wikipedia)
스칸디나비언 수렵그룹인 (Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG))은 BC 6000년 스웨덴 Motala에 묻힌 몇몇 사람들에 의해 대표된다. 그들은 남쪽으로부터 스칸디나비아에 먼저 정착한 Western Hunter-Gatherers의 후손이다. 후에는 노르웨이 해안을 통해 북쪽으로부터 스칸디나비아에 들어온 EHG와 섞였다. (아래 자료 참조)
"Scandinavian Hunter-Gatherer (SHG) is represented by several individuals buried at Motala, Sweden ca. 6000 BC. They were descended from Western Hunter-Gatherers who initially settled Scandinavia from the south, and received later admixture from EHG who entered Scandinavia from the north through the coast of Norway.[72][43][73][47][74] "
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park

Genetic_ancestry_of_hunter-gatherers_dated_between_14_ka_and_9_ka_(SHG) (source : Wikipedia)
서부초원유목민(Western Steppe Herders(WSH)은 Pontic-Caspian steppe지역의 Yamnaya culture(아래 지도 참조)와 긴밀히 관련된 후손들을 나타내는 구별된 조상인자를 가리키는 단어이다. 이 조상은 가끔 Yamnaya ancestry 또는 Steppe ancestry로 언급되는데, EHG와 CHG (Caucasus hunter-gatherer)와 거의 동일한 비율로 형성되어 있다. (아래 자료 참조)
"Western Steppe Herders (WSH) is the name given to a distinct ancestral component that represents descent closely related to the Yamnaya culture of the Pontic–Caspian steppe.[e] This ancestry is often referred to as Yamnaya ancestry or Steppe ancestry, and was formed from EHG and CHG (Caucasus hunter-gatherer) in about equal proportion."
[출처] <펌>Ancient North Eurasian (ANE) (24,000 - 16,000 BP)|작성자 CG Park
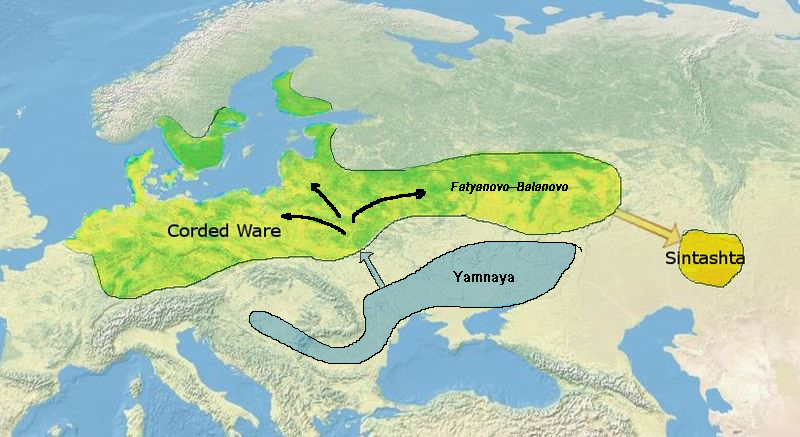
신석기시대의 Yamnaya culture 위치 및 영향 (자료 : 위키피디아)
VI. 고대북유라시언(Ancient North Eurasian, ANE)의 동쪽 이동
고대 북유라시언(ANE)은 동쪽으로도 이동하여 북아메리카로 건너갔다 한다. 아래 지도에서 보듯이 여기에 고대 구석기 시베리아인 (APS, Ancient Paleo-Siberians)과 고대 동북아시아인 (ANEA, Ancient Northern East Asians)이 등장한다.

Map_of_the_Ancient_Paleo-Siberians (source : Wikipedia)
고고학적 유전자 연구에 의하면, 고대 구석기시대 시베리언 (Ancient Paleo-Siberian, APS) 또는 구석기 시베리아인(Paleo-Siberian)은 15000-10000 BP 시기에 북쪽 시베리아와 북동쪽 시베리아에서, 수렵인그룹의 계보를 대표하는 조상 구성요소에 주어진 이름이다. (아래 자료 참조)
"In archaeogenetics, the term Ancient Paleo-Siberian or Paleo-Siberian is the name given to an ancestral component that represents the lineage of the hunter-gatherer people of the 15th-10th millennia before present, in northern and northeastern Siberia."
(source : Ancient Paleo-Siberians, Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lanfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유라시아)
"The Ancient Paleo-Siberian population is thought to have arisen from an Ancient East Asian lineage, which diverged from other East Asian populations sometimes between 26kya to 36kya, and subsequently came into contact and merged with the Ancient North Eurasians (ANE) sometimes between 20kya to 25kya.[2][3][4] The source for the East Asian component among Ancient Paleo-Siberians is to date best represented by Ancient Northern East Asian populations from the Amur region older than 13,000 years, such as AR19K and AR14K, and before the Devil's Cave Ancient Northeast Asian specimens.[5] "
(번역) 고대 구석기 시베리아인(APS)은 고대 동아시아계열로부터 나온 것으로 생각되어진다. 고대 동아시아인은 다른 동아시아으로부터 26000년전-36000년전 사이 어느 시점에 파생하여 그후 20000-25000년전 사이 어느 시기에 고대북유라시언(ANE)와 접하게 되고 혼합된 것으로 판단된다. 고대 구석기 시베리아인(APS) 사이 동아시아인 구성요소 원천은, 13000년전 이전의 아무르지역의 고대동북아시아인(Ancient Northern East Asian, ANEA), 예를 들어 AR19K, AR14K 등과 Devil's cave 고대 동북아시아인 (Ancient Northeast Asian, ANA) 이전의 사람들에 의해 잘 대변된다.
(source : Ancient Paleo-Siberians, Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lanfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유라시아)
"The Ancient Paleo-Siberians are mainly defined by two human archaeological specimens: the 14,000-year-old Ust-Kyakhta-3 (UKY) individual found near Lake Baikal in southern Siberia, and the 9-10,000-year-old Kolyma_M individual found in northeastern Siberia.[5] Specifically, the Lake Baikal Ust'Kyakhta-3 (UKY) specimen (14,050-13,770 BP) was a mixture of 30% ANE ancestry and 70% East Asian ancestry.[1] "
(번역) 고대 구석기 시베리아인은 주로 두 인간 고고학적 표본에 의해 정의되는데: 남시베리아의 바이칼 호수 근처에서 발견된 14000년전의 Ust-Kyakhta-3 (UKY) 인간과 북동시베리아에서 발견된 9000-10000년전의 Kolyma_M 인간이 그 둘이다. 특히, 바이칼호수의 표본 (UstKyakhta-3(UKY), 14050-13770 년전)은 ANE 30%와 동아시아인 70%의 조상유전인자의 혼합이다.
(source : Ancient Paleo-Siberians, Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lanfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유라시아)
"Technologically, Ancient Paleo-Siberians have been associated with microblade technologies and post-Last Glacial Maximum mammoth hunting.[5]
They were later largely replaced by waves of Neo-Siberians, which may be associated with the expansion of early Turkic, Mongolic, and Tungusic speakers, as well as possibly early Yukaghir and Uralic speakers (c. 7–11 kya).[7][8] Ancient Paleo-Siberians, in conjunction with an Inner Northeast Asian (Yumin-like) lineage, gave rise to the Cisbaikal_LNBA ancestry, which may be associated with ancient Yeniseian speakers.[9] "
(번역) 기술적으로, 고대구석기 시베리아인(APS)은 세형돌날 기술과 마지막 절정 빙하기이후 맘모스 사냥과 연관되어 있다. 그들은 대부분 새로운 시베리아인의 흐름에 의해 대체되는데, 이들 새로운 시베리아인은 초기 튀르크, 몽골, 퉁구스어 사용자들의 팽창과 관련되어 있다. 또한 초기 Yukaghir와 우랄어 사용자 (7000-11000년전)와도 관련될 수 있다. 고대 구석기시베리아인(APS)은 내륙의 동북아시아인계열(Yumin과 같은)과 결합하여, 고대 Yeniseian 언어사용자와 관련된 Cisbaikal_LNBA조상인자를 창출했다.
(source : Ancient Paleo-Siberians, Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lanfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유라시아)
"The Ancient Paleo-Siberians are closely related to modern far-northeastern Siberia communities, such as the Koryaks, and to Native Americans.[10][11]
Ancestral Native Americans originated from a similar admixture event as Ancient Paleo-Siberians, carrying c. 67% East Asian-related ancestry and 33% West Eurasian (ANE-like) ancestry.[12] "
(번역) 고대 구석기 시베리아인(APS)은 현대의 극동부 시베리아인 집단, 예를 들면, Koryaks등과 Native Americans과 밀접하게 연관되어 있다.
Native Americans의 조상인자는 고대 구석기 시베리아인(APS)와 유사한 유전자결합에 연원하는데, 동아시아 관련 유전인자 67%, 그리고 서유라시언(ANE와 같은) 조상인자가 33% 를 가지고 있다.
(source : Ancient Paleo-Siberians, Wikipedia, 인용출처 : 필자의 네이버 블로그(lanfos), 카테고리, 구석기 유라시아)
VII. 마무리 말
이상으로 유라시아 대륙의 구석기 시대의 인류이동 역사를 살펴보는 것을 마무리 하고자 한다. 이제까지의 연구는 다음과 같은 요약을 가능하게 한다.
1. 유라시아 대륙의 인류의 두 축은 산동지방의 Tianyuan man (4만년전)과 흑해위 돈강지방의 고대 유럽수렵인계열(Postenki-14 (4만년전))이 있다.
2. 산동지방의 Tianyuan man인류는 동북아시아 아무르지역 인류 (AR33K)와 동북 몽고의 Salkhit인류와 서로 인척관계가 있는 교류집단인 것으로 연구된다.
3. 산동지방의 Tianyuan man 그룹과 흑해위 돈강유역의 고대 유럽수렵인계열의 두 축이 어떻게 교류한 지는 알 수 없으나, 북 시베리아지방의 고대 북유라시언 (Ancient North Eurasian, ANE, 2만4천년전)으로 귀결된다.
4. ANE와 Tianyuan man (또는 다른 초기 구석기시대 동아시아인/동남아시아인 표본) 사이의 유사성이 도출되고 있다.
5. 그러나, ANE로부터 Tianyuan 또는 동아시아인으로의 역방향의 유전자흐름은 그 증거를 발견하지 못했다.
6. 동북아시아의 아무르지역에는 마지막 절정 빙하기가 끝난 후 (19000년전) 새로운 인류가 기존의 인류를 대체한다.
7. 고대 북유라시언(ANE)은 15000년전에 동서로 펴지는데, 5-6천년에 걸쳐 서쪽으로 이동하여 유럽의 동부수렵인그룹(EHG), 스칸디나비아수렵인그룹(SHG), 서부수렵인그룹(WHG)을 이루며, 동쪽으로 이동하여 고대구석기시베리아인(APS)을 이루며, 북아메리카로 넘어가 Native Americans을 이룬다.
8. 현대의 아무르지역 인류는 14000년전의 인류의 유전자그룹이 계속 내려온 현상을 보인다.
9. 동유럽 수렵인그룹(EHG)는 Tianyuan man과 높은 친연성을 보인다. EHGs(Sidelkino)중에서 Tianyuan같은 Basal East Asian 조상인자는 약 12.9%로 추정되었다.
10. 바이칼호수의 표본 (UstKyakhta-3(UKY), 14050-13770 년전)은 ANE 30%와 동아시아인 70%의 조상유전인자의 혼합이다.
'죽엽 단상' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 유전자학으로 살펴 본 신석기 시대 동북아시아 역사 (0) | 2024.03.21 |
|---|---|
| 까치의 강 작수(鵲水)가 흑해 위에 있다 (0) | 2024.01.26 |
| 아틸라 제국과 고구려 (1) | 2024.01.21 |
| 철륵[鐵勒]은 동이의 하나이다 (0) | 2024.01.14 |
| 궁예와 왕건의 모습이 보이는 키예프 루스 (0) | 2024.01.02 |




